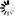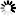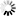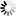──┬─ TRUE ──┬─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤ └─ FALSE ─┘
┌◄──────────────────┐ ──┴─ /12\ ── <digit> ─┴───────────────────────────────────────────────┤
┌◄─────────────────────────────────┐
──┴─┬────────────┬─ /12\ ── <digit> ─┴────────────────────────────────┤
└─ /1\ ── . ─┘── " ─┬────────────────────────────────────────────────┬─ " ──────────┤
│ ┌◄───────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
└─┴─ /1024\ ─┬─ <nonquote EBCDIC character> ─┬─┴─┘
└─ "" ──────────────────────────┘
Explanation
A constant is a literal that contains information and is not changed by any operation. Boolean, integer, real, and string constants are defined in the following discussion.
The following constraints apply to string constants:
-
A pair of quotation marks ("") appearing alone represents a null string (a string of length zero).
-
A pair of quotation marks ("") appearing in a string represents one quotation mark (") within the string.
-
A string constant cannot be broken across a card boundary.
Examples
The following are examples of integer constants:
12
750
12345
The following are examples of real constants:
3.1416
.2
1.0
The following are examples of string constants:
"ABC"
"?*->"
"8-1"