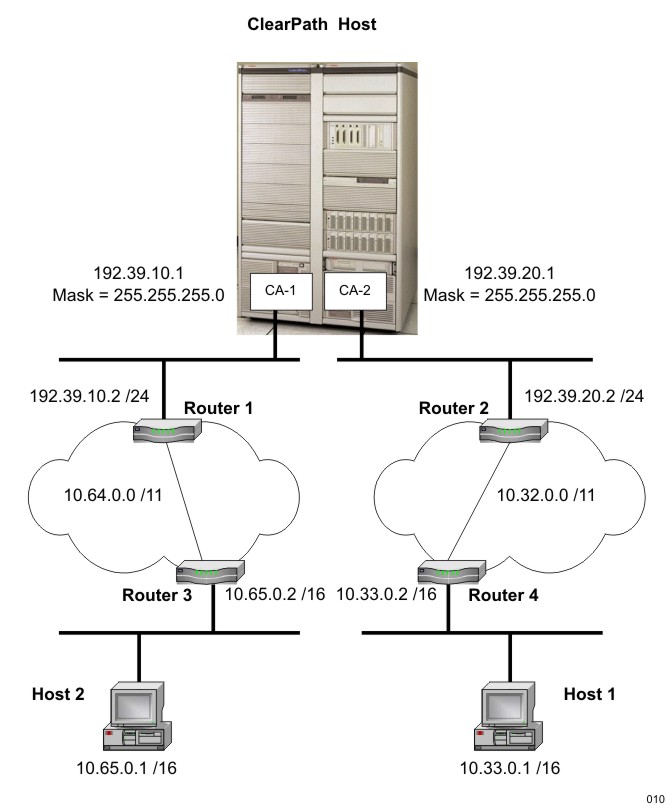
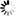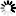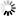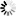In IPv4 networks, VLSM addressing and CIDR routing enable a classful host/server to be configured within a classless network as shown in Mixed Classful and Classless IPv4 Topology.
As illustrated, this topology shows a classful ClearPath server participating within a classless network topology. The ClearPath system is multihomed to two different Class C networks, 192.39.10.0 using CA-1 and 192.39.20.0 using CA-2, both using a classful mask of 255.255.255.0.
Router 1 and Router 2 see the ClearPath system as a member of a /24 CIDR aggregation. Since both Router 1 and Router 2 support VLSM and CIDR, they can easily be configured to match the classful addressing paradigm supported by the ClearPath system (that is, a Class C address with a 24-bit network-prefix can be represented as a /24 CIDR network-prefix) and be able to correctly route datagrams to it.
Router 1 will advertise a route for 192.39.10.0 /24 on its interface to Router 3 and Router 2 will advertise a route for 192.39.20.0 /24 on its interface to Router 4. The Router 1 interface to CA-1 is classful, as is the Router 2 interface to CA-2. On these interfaces, the routers must use RIPv1 to advertise routes. RIPv1 does not include mask information and therefore Router 1 advertises 10.64.0.0 without a mask and Router 2 advertises 10.32.0.0 without a mask.