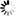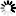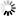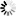IPv6 networks are written using CIDR notation and use the same CIDR technology as is employed by CIDR on IPv4. Under CIDR, IPv6 unicast addresses can be aggregated with prefixes of arbitrary bit length, similar to IPv4 addresses. See Global Unicast Addresses earlier in this section for more details on IPv6 unicast addresses.
An IPv6 network or subnet is a contiguous group of IPv6 addresses the size of which must be a power of two. The initial bits of addresses, which are identical for all hosts in the network, are called the network prefix.
A network is denoted by the first address in the network and the size in bits of the prefix (in decimal), separated with a slash.
For example
2001:0DB8:1234::/48 stands for the network with the addresses
2001:0DB8:1234:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000 through
2001:0DB8:1234:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF
Because a single host can be seen as a network with a 128-bit prefix, you sometimes see host addresses written followed with /128.
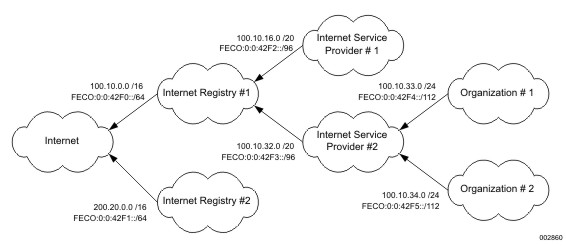
IPv6 CIDR Routing Advertisements shows CIDR routing advertisements with IPv6 addresses added.