An Internet Protocol (IP) address is assigned to every host that uses the TCP/IP IPv4 protocol. This address is 32 bits in length, consisting of four octets or bytes. In decimal form, it is commonly represented as four fields, separated by dots, where each field contains a value in the range of 0 to 255. For example:
192.68.254.17
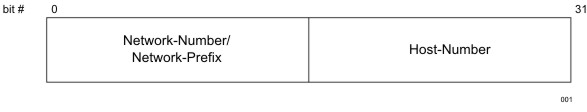
Each IP address consists of two parts as shown in Two-Level Addressing Hierarchy. The first part of the address is the network-number, which identifies the network on the Internet on which the host resides. The second part of the address is the host-number, which indicates a specific host within that network. Since the leading portion of an IP address provides the network-number, it is often referred to as the network-prefix. All hosts on any given network share the same network-prefix but must have a unique host-number.