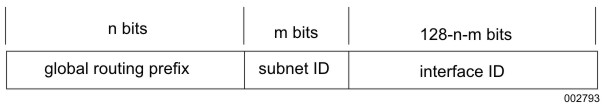
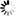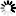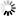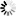The general format for IPv6 global unicast addresses is shown in General Format for Global Unicast Address.
The global routing prefix is a value assigned to a site (a cluster of subnets and links), the subnet ID is an identifier of a link within the site, and the interface ID is used to identify interfaces on a link. See RFC 4291 for a further description of these fields.
All global unicast addresses other than those that start with binary 000 have a 64-bit interface ID field (that is, n + m = 64). Global unicast addresses that start with binary 000 have no such constraint on the size or structure of the interface ID field.
Examples of global unicast addresses that start with binary 000 are the IPv6 address with embedded IPv4 addresses. An example of global addresses starting with a binary value other than 000 (and therefore having a 64-bit interface ID field) can be found in RFC 4291.